if you're new to the scene, the complexity of using protoc to develop a grpc service might have left you feeling overwhelmed. while the protoc compiler is robust, it can be daunting for newcomers. in this series, i'll walk you through my approach to creating grpc services using a tool called skemaloop, demonstrating how straightforward it can be to build such a service.
Understanding gRPCLet's start by exploring the basics of how gRPC functions.
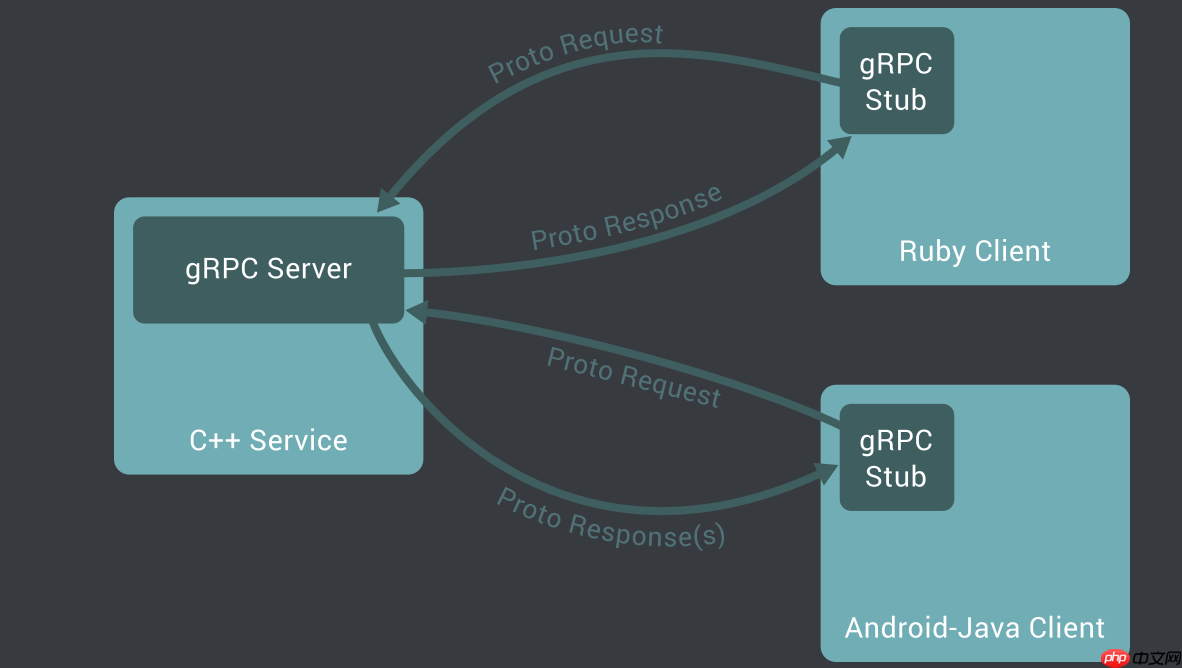 gRPC offers a framework where the IDL (Interface Definition Language) is utilized to outline the service interface and message types. This IDL facilitates the serialization and deserialization of messages between servers and clients. With the protoc compiler, developers can generate boilerplate code for the gRPC server and stub, with all communications managed by the gRPC framework's automatically generated code. There are plenty of resources that delve into the gRPC framework and protobuf IDL, so I won't go into the details here.
gRPC offers a framework where the IDL (Interface Definition Language) is utilized to outline the service interface and message types. This IDL facilitates the serialization and deserialization of messages between servers and clients. With the protoc compiler, developers can generate boilerplate code for the gRPC server and stub, with all communications managed by the gRPC framework's automatically generated code. There are plenty of resources that delve into the gRPC framework and protobuf IDL, so I won't go into the details here.
To create a gRPC server, follow these three steps:
- Define your schema in protobuf.
- Generate the server and stub code.
- Implement your business logic and launch the service.
Defining the SchemaThe official Skemaloop website provides a comprehensive guide to get you started. Click the "try now" button to begin your journey.
You'll need to log in using your GitHub account. Once logged in, you can begin defining your application's interface.
The group will be your GitHub username. For this tutorial, I'll use my sandbox repository for schema definitions. If you wish to establish a hierarchy, you can specify your path; for now, I'll stick with the default.
The module and package structure your schema's hierarchy, with each module containing multiple packages, and each package hosting multiple service definitions, which are essentially multiple protobuf files.
I'll name my service SayHi.
Let's proceed with creating the schema. Below is an example of a schema definition.
代码语言:javascript代码运行次数:0运行复制```javascript syntax = "proto3";//package code generated by schemakit DO NOT EDIT.package sample_module.sample_package;message HelloRequest { string msg = 1;}message HelloReply { string msg = 1; string code = 2;}service SayHi { rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply);}
<code> In the next installment, I'll guide you through the process of generating the server and stub code, and starting the service.</code>






























