在这个项目实战中,我们将继续探讨dataframe的行列索引重排序操作。今天的重点是如何对dataframe进行索引排序和索引输出。让我们开始吧!
数据源
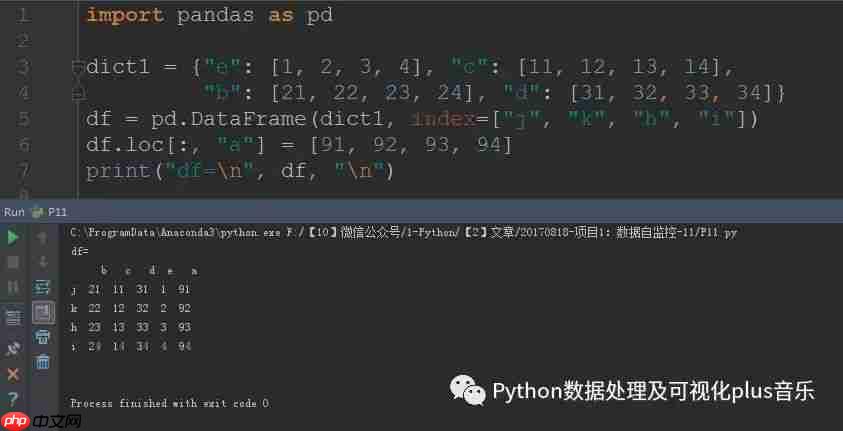
首先,我们需要构建一个DataFrame。我们使用字典来创建DataFrame,并通过
index参数指定行名称。然后,我们通过
loc方法添加一列,以展示后续排序的效果。
import pandas as pd
dict1 = {"e": [1, 2, 3, 4], "c": [11, 12, 13, 14],
"b": [21, 22, 23, 24], "d": [31, 32, 33, 34]}
df = pd.DataFrame(dict1, index=["j", "k", "h", "i"])
df.loc[:, "a"] = [91, 92, 93, 94]
print("df=\n", df, "\n")运行结果:
索引排序
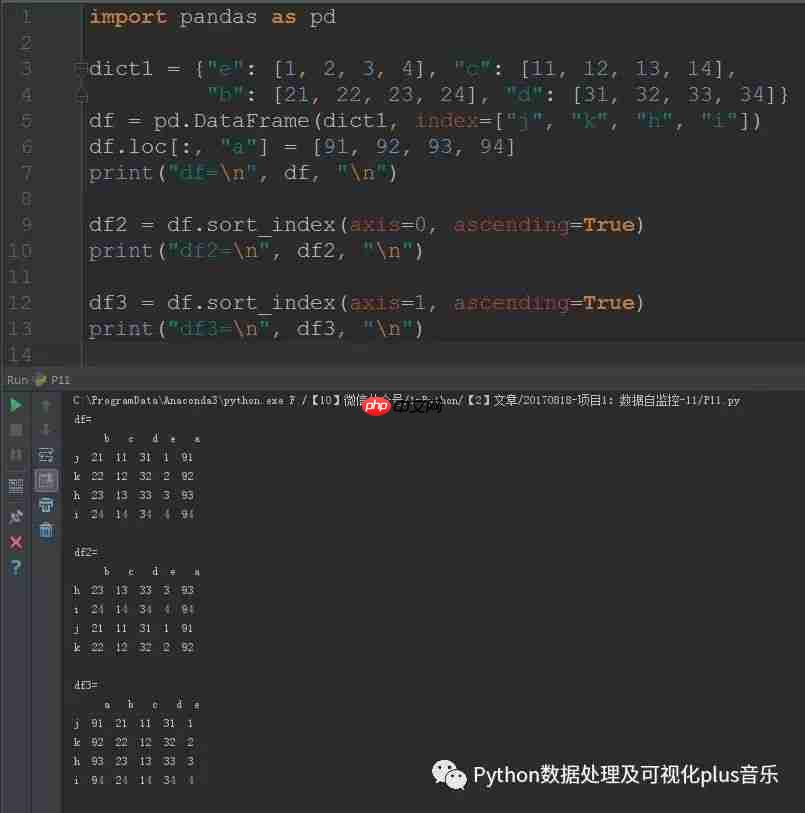
接下来,我们将展示如何对DataFrame的索引进行排序。
sort_index方法可以用来对行索引或列索引进行排序。
df2 = df.sort_index(axis=0, ascending=True)
print("df2=\n", df2, "\n")
df3 = df.sort_index(axis=1, ascending=True)
print("df3=\n", df3, "\n")运行结果:
索引输出
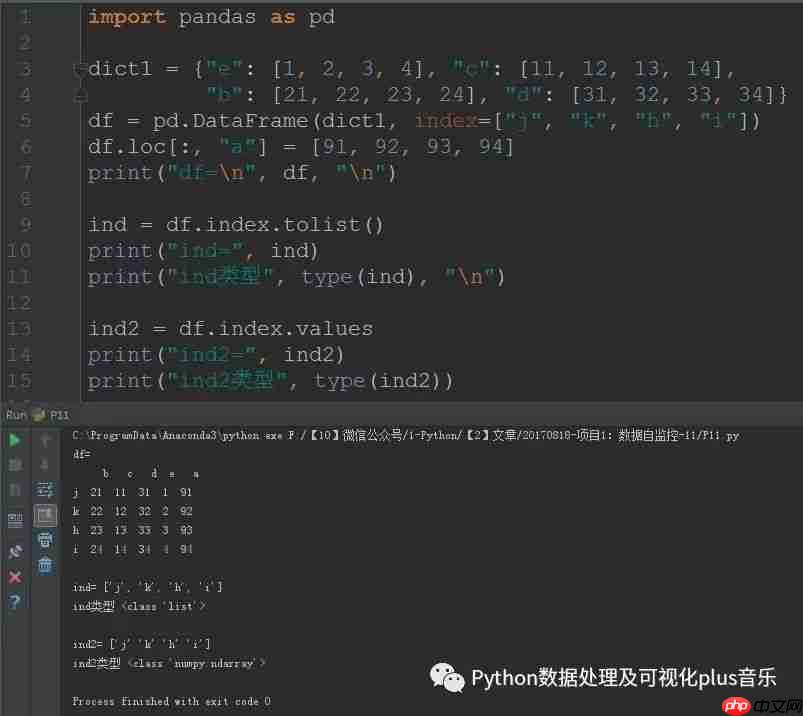
最后,我们将展示如何将DataFrame的索引转化为列表输出。我们可以使用
tolist()方法或
index.values属性来实现这一点。
ind = df.index.tolist()
print("ind=", ind)
print("ind类型", type(ind), "\n")
ind2 = df.index.values
print("ind2=", ind2)
print("ind2类型", type(ind2))运行结果:
通过以上步骤,我们成功地对DataFrame进行了索引排序和索引输出操作。这对于数据处理和分析非常有用,希望这些技巧能帮助您更好地管理和分析数据。






























