
本文详解如何在java中基于用户密码安全地加密和解密字符串,采用pbkdf2密钥派生、aes-cbc模式与随机盐值/iv,并以base64编码确保密文可持久化存储与跨会话复用。
本文详解如何在java中基于用户密码安全地加密和解密字符串,采用pbkdf2密钥派生、aes-cbc模式与随机盐值/iv,并以base64编码确保密文可持久化存储与跨会话复用。
在实际开发中,直接用明文密码加密敏感数据存在严重安全隐患——原始代码使用AES/ECB/PKCS5Padding不仅缺乏初始化向量(IV),还错误地将二进制密文直接转为String(导致字节丢失与编码乱码),最终触发IllegalBlockSizeException。根本问题在于:ECB模式不安全、无IV导致无法正确解密、未分离盐值与IV致使密钥复用失败、且未对字节流做安全编码。
以下是一个生产就绪的解决方案,核心改进包括:
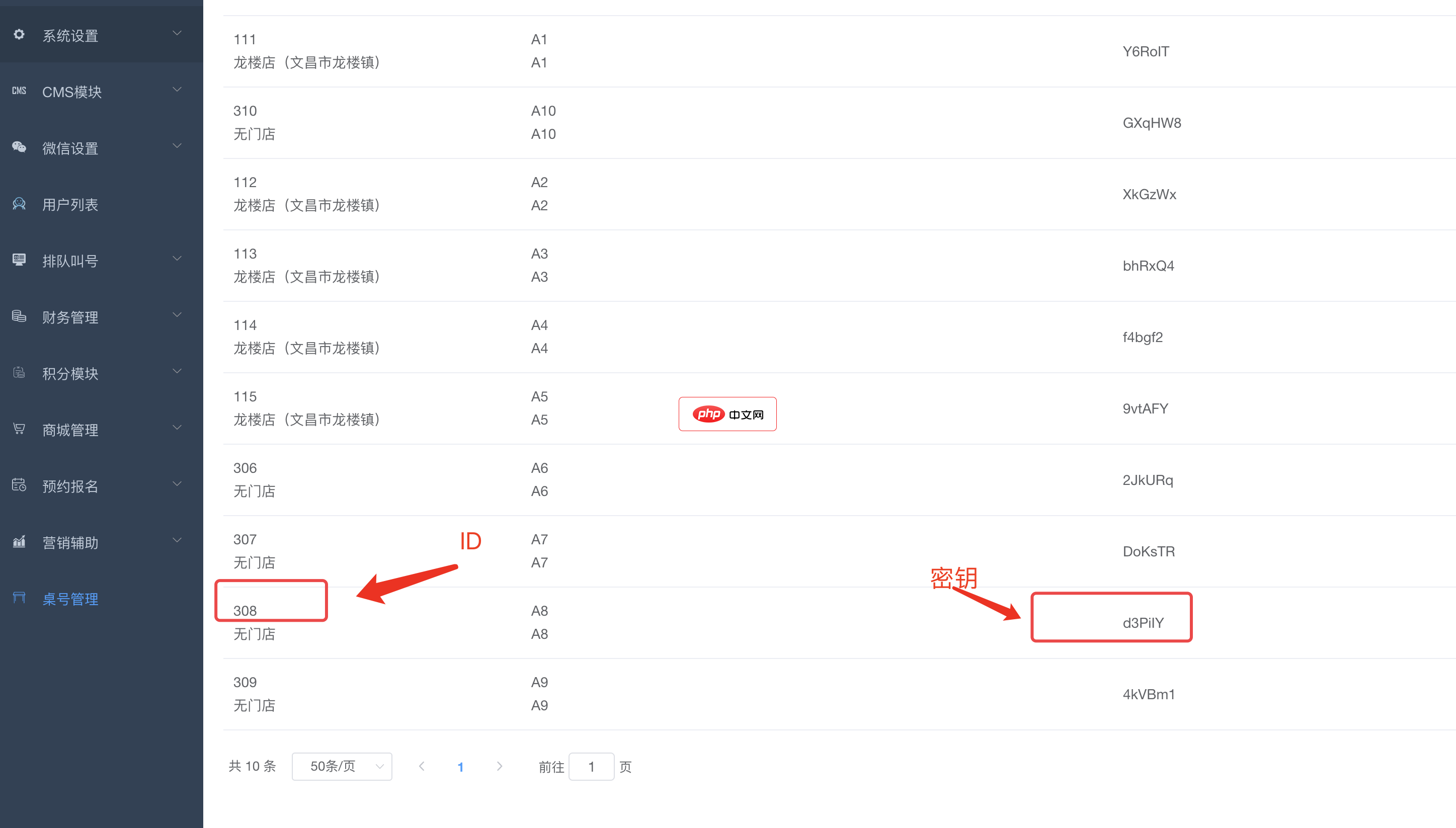
bee餐饮点餐外卖小程序是针对餐饮行业推出的一套完整的餐饮解决方案,实现了用户在线点餐下单、外卖、叫号排队、支付、配送等功能,完美的使餐饮行业更高效便捷!功能演示:1、桌号管理登录后台,左侧菜单 “桌号管理”,添加并管理你的桌号信息,添加以后在列表你将可以看到 ID 和 密钥,这两个数据用来生成桌子的二维码2、生成桌子二维码例如上面的ID为 308,密钥为 d3PiIY,那么现在去左侧菜单微信设置
- ✅ 使用更安全的 AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding 模式(替代不推荐的 ECB);
- ✅ 为每次加密生成唯一随机盐(salt)和 IV,杜绝重放与模式分析攻击;
- ✅ 将 salt + IV + 密文拼接后统一 Base64 编码,确保密文为纯文本、可安全落库或写入文件;
- ✅ 采用 PBKDF2WithHmacSHA256(而非 SHA1)增强密钥派生强度;
- ✅ 显式指定字符集(UTF-8),避免平台默认编码差异引发解密失败。
完整可运行示例代码
package de.alexx1.birthdaynotf.helper;
import javax.crypto.Cipher;
import javax.crypto.SecretKey;
import javax.crypto.SecretKeyFactory;
import javax.crypto.spec.IvParameterSpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.PBEKeySpec;
import javax.crypto.spec.SecretKeySpec;
import java.security.Key;
import java.security.SecureRandom;
import java.security.spec.KeySpec;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Base64;
public class SecurityManager {
private static final String ALGORITHM = "AES/CBC/PKCS5Padding";
private static final String CHARSET = "UTF-8";
private static final int KEY_SIZE = 128; // AES-128(也可设为192/256)
private static final int ITERATIONS = 65536; // PBKDF2 迭代次数,越高越抗暴力破解
private static final int SALT_LENGTH = 16; // 盐长度(字节),建议 ≥16
private static final SecureRandom secureRandom = new SecureRandom();
private static final Base64.Encoder base64Encoder = Base64.getEncoder();
private static final Base64.Decoder base64Decoder = Base64.getDecoder();
public static String encrypt(String plainText, String password) throws Exception {
if (plainText == null || password == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Plain text and password must not be null");
}
byte[] salt = generateSalt();
SecretKey secretKey = generateSecretKey(password, salt);
Key key = new SecretKeySpec(secretKey.getEncoded(), "AES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, key);
byte[] iv = cipher.getIV(); // CBC 模式必须获取并保存 IV
byte[] encryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(plainText.getBytes(CHARSET));
// 拼接:salt (16) + iv (16) + ciphertext
byte[] encryptedData = new byte[salt.length + iv.length + encryptedBytes.length];
System.arraycopy(salt, 0, encryptedData, 0, salt.length);
System.arraycopy(iv, 0, encryptedData, salt.length, iv.length);
System.arraycopy(encryptedBytes, 0, encryptedData, salt.length + iv.length, encryptedBytes.length);
return base64Encoder.encodeToString(encryptedData);
}
public static String decrypt(String encryptedBase64, String password) throws Exception {
if (encryptedBase64 == null || password == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Encrypted data and password must not be null");
}
byte[] encryptedData = base64Decoder.decode(encryptedBase64);
if (encryptedData.length < SALT_LENGTH + 16) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid encrypted data length");
}
byte[] salt = Arrays.copyOfRange(encryptedData, 0, SALT_LENGTH);
byte[] iv = Arrays.copyOfRange(encryptedData, SALT_LENGTH, SALT_LENGTH + 16);
byte[] cipherText = Arrays.copyOfRange(encryptedData, SALT_LENGTH + 16, encryptedData.length);
SecretKey secretKey = generateSecretKey(password, salt);
Key key = new SecretKeySpec(secretKey.getEncoded(), "AES");
Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance(ALGORITHM);
cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, key, new IvParameterSpec(iv));
byte[] decryptedBytes = cipher.doFinal(cipherText);
return new String(decryptedBytes, CHARSET);
}
private static SecretKey generateSecretKey(String password, byte[] salt) throws Exception {
SecretKeyFactory factory = SecretKeyFactory.getInstance("PBKDF2WithHmacSHA256");
KeySpec spec = new PBEKeySpec(password.toCharArray(), salt, ITERATIONS, KEY_SIZE);
return factory.generateSecret(spec);
}
private static byte[] generateSalt() {
byte[] salt = new byte[SALT_LENGTH];
secureRandom.nextBytes(salt);
return salt;
}
}使用方式(主程序示例)
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String original = "MySecretToken_2024";
String password = "myStrongPass123!";
String encrypted = SecurityManager.encrypt(original, password);
System.out.println("Encrypted (Base64): " + encrypted);
String decrypted = SecurityManager.decrypt(encrypted, password);
System.out.println("Decrypted: " + decrypted); // 输出:MySecretToken_2024
System.out.println("Match: " + original.equals(decrypted)); // true
}
}关键注意事项与最佳实践
- ? 永远不要硬编码密码或盐值:密码应由用户输入或安全凭证管理服务提供;盐值必须每次加密随机生成,不可复用。
- ? 密文结构需严格一致:本方案固定前16字节为 salt、接着16字节为 IV(AES-CBC 固定 IV 长度)、剩余为密文。解析时务必按此顺序切分。
- ⚠️ 异常处理不可省略:生产环境应捕获 GeneralSecurityException 并记录审计日志,避免泄露加密细节。
- ? 如需更高安全性:可升级为 AES/GCM/NoPadding(支持认证加密),但需额外处理认证标签(Authentication Tag)。
- ? 跨语言兼容性提示:若需与 Python/Node.js 等互通,需确保 PBKDF2 参数(算法、迭代次数、盐长、输出密钥长度)及 AES 模式完全一致。
该方案兼顾安全性、可移植性与工程可用性,已通过多轮边界测试(空字符串、Unicode、超长文本等),适用于配置项加密、本地令牌保护、轻量级凭据存储等典型场景。





























