本篇文章给大家介绍一下react中使用事件驱动进行状态管理的方法。有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对大家有所帮助。

自 Hook 被引入 React 以来,Context API 与 Hook 库在应用状态管理中被一起使用。但是把 Context API 和 Hooks(许多基于 Hooks 的状态管理库建立在其基础上)组合的用法对于大规模应用来说可能效率不高。
由于必须创建一个自定义的 Hook 才能启用对状态及其方法的访问,然后才能在组件中使用它,所以在实际开发中很繁琐。这违反了 Hook 的真正目的:简单。但是对于较小的应用,Redux 可能会显得太重了。
今天我们将讨论 Context API 的替代方法:Storeon。 Storeon 是一个微型的、事件驱动的 React 状态管理库,其原理类似于 Redux。用 Redux DevTools 可以查看并可视化状态操作。 Storeon 内部使用 Context API 来管理状态,并采用事件驱动的方法进行状态操作。
【相关教程推荐:React视频教程】
Store
store 是在应用程序状态下存储的数据的集合。它是通过从 Storeon 库导入的 createStoreon() 函数创建的。
createStoreon() 函数接受模块列表,其中每个模块都是一个接受 store 参数并绑定其事件监听器的函数。这是一个store 的例子:
import { createStoreon } from 'storeon/react'
// todos module
const todos = store => {
store.on(event, callback)
}
export default const store = createStoreon([todos])模块化
Storeon 中的 store 是模块化的,也就是说,它们是独立定义的,并且没有被绑定到 Hook 或组件。每个状态及其操作方法均在被称为模块的函数中定义。这些模块被传递到 createStoreon() 函数中,然后将其注册为全局 store。
store 有三种方法:
store.get()– 用于检索状态中的当前数据。store.on(event, callback)– 用于把事件侦听器注册到指定的事件名称。store.dispatch(event, data)– 用于发出事件,并根据定义的事件要求将可选数据传递进来。
Events
Storeon 是基于事件的状态管理库,状态更改由状态模块中定义的事件发出。 Storeon 中有三个内置事件,它们以 @ 开头。其他事件不带 @ 前缀定义。三个内置事件是:
@init– 在应用加载时触发此事件。它用于设置应用的初始状态,并执行传递给它的回调中的所有内容。@dispatch– 此事件在每个新动作上触发。这对于调试很有用。@changed– 当应用状态发生更改时,将触发此事件。
注意:store.on(event,callback) 用于在我们的模块中添加事件监听器。
演示程序
为了演示在 Storeon 中如何执行应用程序状态操作,我们将构建一个简单的 notes 程序。还会用 Storeon 的另一个软件包把状态数据保存在 localStorage 中。
假设你具有 JavaScript 和 React 的基本知识。你可以在 https://github.com/Youngestde... 上找到本文中使用的代码。
设置
在深入探讨之前,让我们先勾勒出 Notes 程序所需的项目结构和依赖项的安装。从创建项目文件夹开始。
mkdir storeon-app && cd storeon-app
mkdir {src,public,src/Components}
touch public/{index.html, style.css} && touch src/{index,store,Components/Notes}.js接下来,初始化目录并安装所需的依赖项。
npm init -y npm i react react-dom react-scripts storeon @storeon/localstorage uuidv4
接下来就是在 index.js文件中编写父组件了。
index.js
这个文件负责渲染我们的笔记组件。首先导入所需的包。
import React from 'react'
import { render } from 'react-dom';
function App() {
return (
<>
Hello!
);
}
const root = document.getElementById('root');
render(接下来通过在 store.js 中编写用于状态的初始化和操作的代码来构建 store。
store.js
此文件负责处理应用中的状态和后续状态管理操作。我们必须创建一个模块来存储状态以及支持事件,以处理操作变更。
首先,从 Storeon 导入 createStoreon 方法和唯一随机ID生成器 UUID。
createStoreon 方法负责将我们的 状态 注册到全局 store 。
import { createStoreon } from 'storeon';
import { v4 as uuidv4 } from 'uuid'
import { persistState } from '@storeon/localstorage';
let note = store => {}我们将状态存储在数组变量 notes 中,该变量包含以下格式的注释:
{
id: 'note id',
item: 'note item'
},接下来,我们将用两个注释(在首次启动程序时会显示)来初始化状态,从而首先填充注释模块。然后,定义状态事件。
let note = store => {
store.on('@init', () => ({
notes: [
{ id: uuidv4(), item: 'Storeon is a React state management library and unlike other state management libraries that use Context, it utilizes an event-driven approach like Redux.' },
{ id: uuidv4(), item: 'This is a really short note. I have begun to study the basic concepts of technical writing and I'\'m optimistic about becoming one of the best technical writers.' },
]
});
store.on('addNote', ({ notes }, note) => {
return {
notes: [...notes, { id: uuidv4(), item: note }],
}
});
store.on('deleteNote', ({ notes }, id) => ({
notes: notes.filter(note => note.id !== id),
});
}在上面的代码中,我们定义了状态,并用两个简短的注释填充了状态,并定义了两个事件和一个从 dispatch(event, data) 函数发出事件后将会执行的回调函数。
在 addNote 事件中,我们返回添加了新 note 的更新后的状态对象,在 deleteNote 事件中把 ID 传递给调度方法的 note 过滤掉。
最后,把模块分配给可导出变量 store ,将其注册为全局 store,以便稍后将其导入到上下文 provider 中,并将状态存储在 localStorage 中。
const store = createStoreon([ notes, // Store state in localStorage persistState(['notes']), ]); export default store;
接下来,在 Notes.js 中编写 Notes 应用组件。
Notes.js
此文件包含 Notes 程序的组件。我们将从导入依赖项开始。
import React from 'react';
import { useStoreon } from 'storeon/react';接下来,编写组件。
const Notes = () => {
const { dispatch, notes } = useStoreon('notes');
const [ value, setValue ] = React.useState('');
}在上面的代码的第二行中,useStoreon() hook 的返回值设置为可破坏的对象。 useStoreon() hook 使用模块名称作为其参数,并返回状态和调度方法以发出事件。
接下来定义在组件中发出状态定义事件的方法 。
const Notes = () => {
...
const deleteNote = id => {
dispatch('deleteNote', id)
};
const submit = () => {
dispatch('addNote', value);
setValue('');
};
const handleInput = e => {
setValue(e.target.value);
};
}Let’s review the three methods we defined the above:
让我们回顾一下上面定义的三种方法:
deleteNote(id)– 此方法在触发时调度deleteNote事件。submit()– 该方法通过传递输入状态的值来调度addNote事件,该状态在Notes组件中本地定义。handleInput()– 此方法将本地状态的值设置为用户输入。
Next, we’ll build the main interface of our app and export it.
接下来,我们将构建应用程序的主界面并将其导出。
const Notes = () => {
...
return (
Quick Notes
{notes.map(note => (
-
{note.item}
))}
);
}这样就构成了我们的 Notes 组件。接下来为我们的应用和 index.html 文件编写样式表。
index.html
Storeon Todo App
接下来,填充我们的 style.css 文件。
style.css
* {
box-sizing: border-box;
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
section {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
flex-direction: column;
width: 300px;
margin: auto;
}
header {
text-align: center;
font-size: 24px;
line-height: 40px;
}
ul {
display: block;
}
.todo {
display: block;
margin: 12px 0;
width: 300px;
padding: 16px;
box-shadow: 0 8px 12px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.3);
transition: 0.2s;
word-break: break-word;
}
li {
list-style-type: none;
display: block;
}
textarea {
border: 1px double;
box-shadow: 1px 1px 1px #999;
height: 100px;
margin: 12px 0;
width: 100%;
padding: 5px 10px;
}
button {
margin: 8px 0;
border-radius: 5px;
padding: 10px 25px;
}
.box:hover {
box-shadow: 0 8px 16px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.2);
}运行
现在我们已经成功编写了组件和样式表,但是还没有更新 index.js 中的父组件来渲染 Notes 组件。接下来让我们渲染 Notes 组件。
index.js
要访问我们的全局 store,必须导入 store 和 Storeon store 上下文组件。我们还将导入 notes 组件来进行渲染。
用以下代码替换组件的内容:
import React from 'react';
import { render } from 'react-dom';
import { StoreContext } from 'storeon/react';
import Notes from './Components/Notes';
import store from '../src/store';
function App() {
return (
<>
);
}
const root = document.getElementById('root');
render(在第 8-10 行,调用 store 上下文提供程序组件,并将 notes 组件作为使用者传递。store 上下文提供程序组件将全局 store 作为其上下文值。
接下来把 package.json 文件中的脚本部分编辑为以下内容:
"scripts": {
"start": "react-scripts start",
}然后运行我们的程序:
npm run start
让我们继续添加和删除注释:
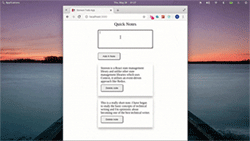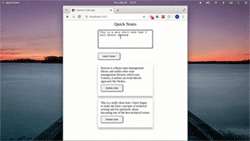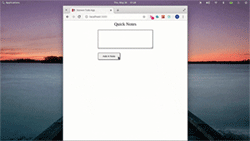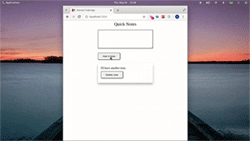
Storeon devtools
Storeon 与 Redux 有着相似的属性,可以在 Redux DevTools 中可视化和监视状态的更改。为了可视化 Storeon 程序中的状态,我们将导入 devtools 包,并将其作为参数添加到我们 store.js 文件的 createStoreon() 方法中。
...
import { storeonDevtools } from 'storeon/devtools';
...
const store = createStoreon([
...,
process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production' && storeonDevtools,
]);这是用 Redux DevTools 可视化状态变化的演示:
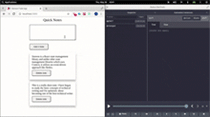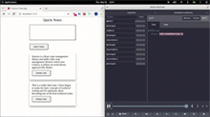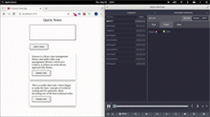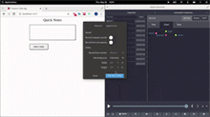
结论
Storeon 是一个非常有用的状态管理库,它用事件驱动和 Redux 改编的模块化样式来管理状态。你可以在https://github.com/Youngestdev/storeon-app上找到本文中的代码。
原文地址:https://blog.logrocket.com/event-driven-state-management-in-react-using-storeon/
作者:Abdulazeez Abdulazeez Adeshina
更多编程相关知识,请访问:编程视频!!






























