引言:
在Sping中,一般使用<bean>这样的元素来配置一个bean,Spring在创建容器的时候会扫描这些配置,根据配置创建对象存放于容器中,然后我们再从容器中取出,或者在配置其他bean的时候作为属性注入。使用bean配置的一个限制是我们必须遵循配置文件的XML Schema定义,这在大多数情况下不会出现问题。但是在一些情况下,我们希望实现更为灵活的bean配置。Spring为此提供了 Custom tag Support,也称为Extensible XML Authoring。通过这个拓展点,我们可以灵活定制自己需要的配置格式。
例如,如果我们使用了责任链设计应用程序,那么我们可能希望用下面的方式来配置责任链:
<chain id="orderChain" class="foo.bar">
<handler> handler1</handler>
<hadnler> handler2</handler>
</chain>档Spring创建容器时,扫描到这样的元素的时候,会根据我们事先的定义实例化一个责任链对象,并填充属性。因此,这种特殊的<chain>标签可以作为<bean>标签以外的另一种形式。借助Spring的Custome Tag,我们完全可以实现这样的bean配置。在产品级的应用框架中,可以实现更为复杂的定制标签元素。作为一个入门级别的介绍,我们定义一个用于配置日期格式化的一个类SimpleDateFormat。当然,使用传统的<bean>完全够用,我们这里只是作为例子。
一个HelloWorld例子:
立即学习“Java免费学习笔记(深入)”;
定制标签的第一步是要定义标签元素的XML结构,也就是采用XSD来元素我们要定制的元素的结构时怎样的。
我们定义如下一个简单的XSD:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsd:schema xmlns="http://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
targetNamespace="http://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns"
elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDefault="unqualified">
<xsd:import namespace="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"/>
<xsd:element name="dateformat">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexContent>
<xsd:extension base="beans:identifiedType">
<xsd:attribute name="lenient" type="xsd:boolean"/>
<xsd:attribute name="pattern" type="xsd:string" use="required"/>
</xsd:extension>
</xsd:complexContent>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
</xsd:schema>在这个XSD定义中,有一个标签叫dateformat,这就是我们用来替换bean标签的自定义标签。注意到我们导入了Spring本身的beans命名空间,并且在beans:identifiedType基础之上定义dateformat标签。也就是我们这个标签可以像<bean>标签一样拥有id属性。同时我们增加了两个属性lenient和pattern。这有点继承的味道。
定义完XSD之后,我们要告诉Spring遇到这样的标记(命名空间+元素名称)时,如何创建对象。Spring中,完成这个任务的是NamespaceHandler。因此我们需要提供一个NamespaceHandler实现来处理自定义的<dateformat>标签元素。
一个简单的实现如下:
package extensiblexml.customtag;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.NamespaceHandlerSupport;
public class MyNamespaceHandler extends NamespaceHandlerSupport {
public void init() {
registerBeanDefinitionParser("dateformat",
new SimpleDateFormatBeanDefinitionParser());
}
}我们在初始化方法中注册了一个Bean定义的解析器,这个解析器就是用来解析定制的配置标签的。
其实现如下:
package extensiblexml.customtag;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionBuilder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser;
import org.springframework.util.StringUtils;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public class SimpleDateFormatBeanDefinitionParser extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser {
protected Class<SimpleDateFormat> getBeanClass(Element element) {
return SimpleDateFormat.class;
}
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
protected void doParse(Element element, BeanDefinitionBuilder bean) {
// this will never be null since the schema explicitly requires that a value be supplied
String pattern = element.getAttribute("pattern");
bean.addConstructorArg(pattern);
// this however is an optional property
String lenient = element.getAttribute("lenient");
if (StringUtils.hasText(lenient)) {
bean.addPropertyValue("lenient", Boolean.valueOf(lenient));
}
}
}这个解析器的doParse中,实现了解析的具体逻辑,借助Spring提供的支持类,我们可以很轻松地完成解析。以上三个文件放在同一个目录下,即把XSD文件跟Java代码放在同一目录。编码完毕之后,还需要做一些配置工作。我们必须告诉Spring我们准备使用自定义的标签元素,告诉Spring如何解析元素,否则Spring没那么聪明。这里需要2个配置文件,在与代码根路径同一级别下,床垫一个叫META-INF的文件。并在里面创建名为spring.handlers和spring.schemas,用于告诉Spring自定义标签的文档结构以及解析它的类。两个文件内容分别如下:
spring.handlers:
http\://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns=extensiblexml.customtag.MyNamespaceHandler
等号的左边是XSD定义中的targetNamespace属性,右边是NamespaceHandler的全称限定名。
spring.schemas:
http\://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns/myns.xsd=extensiblexml/customtag/myns.xsd
然后像往常一样配置bean,作为简单的测试,我们定义一个bean:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:myns="http://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns http://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns/myns.xsd" > <myns:dateformat id="defaultDateFormat" pattern="yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm" lenient="true" /> </beans>
在Eclipse中,整个项目结构如下图:
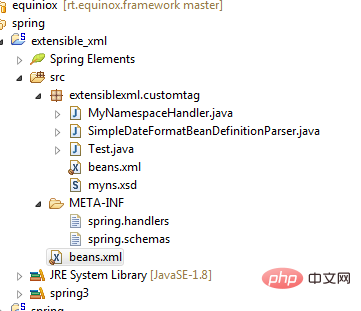
最后我们写个测试类测试一下能否工作:
package extensiblexml.customtag;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(
"beans.xml");
SimpleDateFormat format = (SimpleDateFormat) context
.getBean("defaultDateFormat");
System.out.println(format.format(new Date()));
}
}一切正常,输出如下:
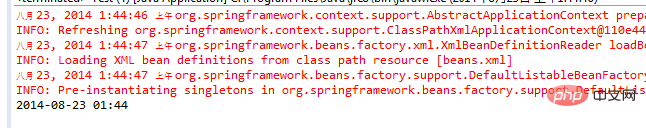
更实用的例子
第一个例子主要是为了举例,在实际中用处不大,我们接着来看一个更复杂的自定义标签。我们自定义一个<fileList>标签,当Spring扫描到这个标签的时候,创建一个指定目录下的File类的集合。另外,可以使用<fileFilter>对该目录的文件进行过滤。
如下:
<core-commons:fileList id="xmlList" directory="src/extensiblexml/example">
<core-commons:fileFilter>
<bean class="org.apache.commons.io.filefilter.RegexFileFilter">
<constructor-arg value=".*.java" />
</bean>
</core-commons:fileFilter>
</core-commons:fileList>上面的bean定义中,我们从“src/extensible/example”目录中筛选出java源码文件。
使用下面的测试迭代输出文件名:
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<File> fileList = (List<File>) context.getBean("xmlList");
for (File file : fileList) {
System.out.println(file.getName());
}输出结果如下:
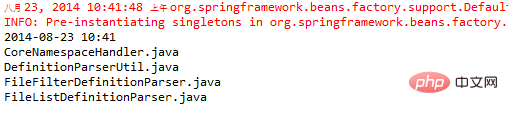
根据第一个例子中的步骤,各部分配置及代码如下:
core-commons-1.0.xsd:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<xsd:schema xmlns="http://www.example.com/schema/core-commons-1.0"
targetNamespace="http://www.example.com/schema/core-commons-1.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:xsd="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema"
xmlns:beans="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
elementFormDefault="qualified"
attributeFormDefault="unqualified"
version="1.0">
<xsd:import namespace="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd"/>
<xsd:element name="fileList">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexContent>
<xsd:extension base="beans:identifiedType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:element ref="fileFilter" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="1"/>
<xsd:element ref="fileList" minOccurs="0" maxOccurs="unbounded"/>
</xsd:sequence>
<xsd:attribute name="directory" type="xsd:string"/>
<xsd:attribute name="scope" type="xsd:string"/>
</xsd:extension>
</xsd:complexContent>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:element name="fileFilter">
<xsd:complexType>
<xsd:complexContent>
<xsd:extension base="beans:identifiedType">
<xsd:group ref="limitedType"/>
<xsd:attribute name="scope" type="xsd:string"/>
</xsd:extension>
</xsd:complexContent>
</xsd:complexType>
</xsd:element>
<xsd:group name="limitedType">
<xsd:sequence>
<xsd:choice minOccurs="1" maxOccurs="unbounded">
<xsd:element ref="beans:bean"/>
<xsd:element ref="beans:ref"/>
<xsd:element ref="beans:idref"/>
<xsd:element ref="beans:value"/>
<xsd:any minOccurs="0"/>
</xsd:choice>
</xsd:sequence>
</xsd:group>
</xsd:schema>CoreNamespaceHandler.java:
package extensiblexml.example;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.NamespaceHandlerSupport;
public class CoreNamespaceHandler
extends NamespaceHandlerSupport
{
@Override
public void init() {
this.registerBeanDefinitionParser("fileList", new FileListDefinitionParser());
this.registerBeanDefinitionParser("fileFilter", new FileFilterDefinitionParser());
}
}FileListDefinitionParser.java:
public class FileListDefinitionParser
extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser
{
/**
* The bean that is created for this tag element
*
* @param element The tag element
* @return A FileListFactoryBean
*/
@Override
protected Class<?> getBeanClass(Element element) {
return FileListFactoryBean.class;
}
/**
* Called when the fileList tag is to be parsed
*
* @param element The tag element
* @param ctx The context in which the parsing is occuring
* @param builder The bean definitions build to use
*/
@Override
protected void doParse(Element element, ParserContext ctx, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) {
// Set the directory property
builder.addPropertyValue("directory", element.getAttribute("directory"));
// Set the scope
builder.setScope(element.getAttribute("scope"));
// We want any parsing to occur as a child of this tag so we need to make
// a new one that has this as it's owner/parent
ParserContext nestedCtx = new ParserContext(ctx.getReaderContext(), ctx.getDelegate(), builder.getBeanDefinition());
// Support for filters
Element exclusionElem = DomUtils.getChildElementByTagName(element, "fileFilter");
if (exclusionElem != null) {
// Just make a new Parser for each one and let the parser do the work
FileFilterDefinitionParser ff = new FileFilterDefinitionParser();
builder.addPropertyValue("filters", ff.parse(exclusionElem, nestedCtx));
}
// Support for nested fileList
List<Element> fileLists = DomUtils.getChildElementsByTagName(element, "fileList");
// Any objects that created will be placed in a ManagedList
// so Spring does the bulk of the resolution work for us
ManagedList<Object> nestedFiles = new ManagedList<Object>();
if (fileLists.size() > 0) {
// Just make a new Parser for each one and let them do the work
FileListDefinitionParser fldp = new FileListDefinitionParser();
for (Element fileListElem : fileLists) {
nestedFiles.add(fldp.parse(fileListElem, nestedCtx));
}
}
// Support for other tags that return File (value will be converted to file)
try {
// Go through any other tags we may find. This does not mean we support
// any tag, we support only what parseLimitedList will process
NodeList nl = element.getChildNodes();
for (int i=0; i<nl.getLength(); i++) {
// Parse each child tag we find in the correct scope but we
// won't support custom tags at this point as it coudl destablize things
DefinitionParserUtil.parseLimitedList(nestedFiles, nl.item(i), ctx,
builder.getBeanDefinition(), element.getAttribute("scope"), false);
}
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
// Set the nestedFiles in the properties so it is set on the FactoryBean
builder.addPropertyValue("nestedFiles", nestedFiles);
}
public static class FileListFactoryBean
implements FactoryBean<Collection<File>>
{
String directory;
private Collection<FileFilter> filters;
private Collection<File> nestedFiles;
@Override
public Collection<File> getObject() throws Exception {
// These can be an array list because the directory will have unique's and the nested is already only unique's
Collection<File> files = new ArrayList<File>();
Collection<File> results = new ArrayList<File>(0);
if (directory != null) {
// get all the files in the directory
File dir = new File(directory);
File[] dirFiles = dir.listFiles();
if (dirFiles != null) {
files = Arrays.asList(dirFiles);
}
}
// If there are any files that were created from the nested tags,
// add those to the list of files
if (nestedFiles != null) {
files.addAll(nestedFiles);
}
// If there are filters we need to go through each filter
// and see if the files in the list pass the filters.
// If the files does not pass any one of the filters then it
// will not be included in the list
if (filters != null) {
boolean add;
for (File f : files) {
add = true;
for (FileFilter ff : filters) {
if (!ff.accept(f)) {
add = false;
break;
}
}
if (add) results.add(f);
}
return results;
}
return files;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return Collection.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return false;
}
public void setDirectory(String dir) {
this.directory = dir;
}
public void setFilters(Collection<FileFilter> filters) {
this.filters = filters;
}
/**
* What we actually get from the processing of the nested tags
* is a collection of files within a collection so we flatten it and
* only keep the uniques
*/
public void setNestedFiles(Collection<Collection<File>> nestedFiles) {
this.nestedFiles = new HashSet<File>(); // keep the list unique
for (Collection<File> nested : nestedFiles) {
this.nestedFiles.addAll(nested);
}
}
}
}FileFilterDefinitionParser.java
public class FileFilterDefinitionParser
extends AbstractSingleBeanDefinitionParser
{
/**
* The bean that is created for this tag element
*
* @param element The tag element
* @return A FileFilterFactoryBean
*/
@Override
protected Class<?> getBeanClass(Element element) {
return FileFilterFactoryBean.class;
}
/**
* Called when the fileFilter tag is to be parsed
*
* @param element The tag element
* @param ctx The context in which the parsing is occuring
* @param builder The bean definitions build to use
*/
@Override
protected void doParse(Element element, ParserContext ctx, BeanDefinitionBuilder builder) {
// Set the scope
builder.setScope(element.getAttribute("scope"));
try {
// All of the filters will eventually end up in this list
// We use a 'ManagedList' and not a regular list because anything
// placed in a ManagedList object will support all of Springs
// functionalities and scopes for us, we dont' have to code anything
// in terms of reference lookups, EL, etc
ManagedList<Object> filters = new ManagedList<Object>();
// For each child node of the fileFilter tag, parse it and place it
// in the filtes list
NodeList nl = element.getChildNodes();
for (int i=0; i<nl.getLength(); i++) {
DefinitionParserUtil.parseLimitedList(filters, nl.item(i), ctx, builder.getBeanDefinition(), element.getAttribute("scope"));
}
// Add the filtes to the list of properties (this is applied
// to the factory beans setFilters below)
builder.addPropertyValue("filters", filters);
}
catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public static class FileFilterFactoryBean
implements FactoryBean<Collection<FileFilter>>
{
private final List<FileFilter> filters = new ArrayList<FileFilter>();
@Override
public Collection<FileFilter> getObject() throws Exception {
return filters;
}
@Override
public Class<?> getObjectType() {
return Collection.class;
}
@Override
public boolean isSingleton() {
return false;
}
/**
* Go through the list of filters and convert the String ones
* (the ones that were set with <value> and make them NameFileFilters
*/
public void setFilters(Collection<Object> filterList) {
for (Object o : filterList) {
if (o instanceof String) {
filters.add(new NameFileFilter(o.toString()));
}
else if (o instanceof FileFilter) {
filters.add((FileFilter)o);
}
}
}
}
}DefinitionParserUtil.java:
package extensiblexml.example;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinition;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanDefinitionHolder;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.BeanDefinitionReaderUtils;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.support.ManagedList;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.BeanDefinitionParserDelegate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.ParserContext;
import org.springframework.expression.Expression;
import org.springframework.expression.ExpressionParser;
import org.springframework.expression.spel.standard.SpelExpressionParser;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
public class DefinitionParserUtil {
/**
* Parses the children of the passed in ParentNode for the following tags:
* <br/>
* value
* ref
* idref
* bean
* property
* *custom*
* <p/>
*
* The value tag works with Spring EL even in a Spring Batch scope="step"
*
* @param objects The list of resultings objects from the parsing (passed in for recursion purposes)
* @param parentNode The node who's children should be parsed
* @param ctx The ParserContext to use
* @param parentBean The BeanDefinition of the bean who is the parent of the parsed bean
* (i.e. the Bean that is the parentNode)
* @param scope The scope to execute in. Checked if 'step' to provide Spring EL
* support in a Spring Batch env
* @throws Exception
*/
public static void parseLimitedList(ManagedList<Object> objects, Node node,
ParserContext ctx, BeanDefinition parentBean, String scope)
throws Exception
{
parseLimitedList(objects, node, ctx, parentBean, scope, true);
}
/**
* Parses the children of the passed in ParentNode for the following tags:
* <br/>
* value
* ref
* idref
* bean
* property
* *custom*
* <p/>
*
* The value tag works with Spring EL even in a Spring Batch scope="step"
*
* @param objects The list of resultings objects from the parsing (passed in for recursion purposes)
* @param parentNode The node who's children should be parsed
* @param ctx The ParserContext to use
* @param parentBean The BeanDefinition of the bean who is the parent of the parsed bean
* (i.e. the Bean that is the parentNode)
* @param scope The scope to execute in. Checked if 'step' to provide Spring EL
* support in a Spring Batch env
* @param supportCustomTags Should we support custom tags within our tags?
* @throws Exception
*/
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public static void parseLimitedList(ManagedList<Object> objects, Node node,
ParserContext ctx, BeanDefinition parentBean, String scope, boolean supportCustomTags)
throws Exception
{
// Only worry about element nodes
if (node.getNodeType() == Node.ELEMENT_NODE) {
Element elem = (Element)node;
String tagName = node.getLocalName();
if (tagName.equals("value")) {
String val = node.getTextContent();
// to get around an issue with Spring Batch not parsing Spring EL
// we will do it for them
if (scope.equals("step")
&& (val.startsWith("#{") && val.endsWith("}"))
&& (!val.startsWith("#{jobParameters"))
)
{
// Set up a new EL parser
ExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
// Parse the value
Expression exp = parser.parseExpression(val.substring(2, val.length()-1));
// Place the results in the list of created objects
objects.add(exp.getValue());
}
else {
// Otherwise, just treat it as a normal value tag
objects.add(val);
}
}
// Either of these is a just a lookup of an existing bean
else if (tagName.equals("ref") || tagName.equals("idref")) {
objects.add(ctx.getRegistry().getBeanDefinition(node.getTextContent()));
}
// We need to create the bean
else if (tagName.equals("bean")) {
// There is no quick little util I could find to create a bean
// on the fly programmatically in Spring and still support all
// Spring functionality so basically I mimic what Spring actually
// does but on a smaller scale. Everything Spring allows is
// still supported
// Create a factory to make the bean
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = new DefaultListableBeanFactory();
// Set up a parser for the bean
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate pd = new BeanDefinitionParserDelegate(ctx.getReaderContext());
// Parse the bean get its information, now in a DefintionHolder
BeanDefinitionHolder bh = pd.parseBeanDefinitionElement(elem, parentBean);
// Register the bean will all the other beans Spring is aware of
BeanDefinitionReaderUtils.registerBeanDefinition(bh, beanFactory);
// Get the bean from the factory. This will allows Spring
// to do all its work (EL processing, scope, etc) and give us
// the actual bean itself
Object bean = beanFactory.getBean(bh.getBeanName());
objects.add(bean);
}
/*
* This is handled a bit differently in that it actually sets the property
* on the parent bean for us based on the property
*/
else if (tagName.equals("property")) {
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate pd = new BeanDefinitionParserDelegate(ctx.getReaderContext());
// This method actually set eh property on the parentBean for us so
// we don't have to add anything to the objects object
pd.parsePropertyElement(elem, parentBean);
}
else if (supportCustomTags) {
// handle custom tag
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate pd = new BeanDefinitionParserDelegate(ctx.getReaderContext());
BeanDefinition bd = pd.parseCustomElement(elem, parentBean);
objects.add(bd);
}
}
}
}spring.schemas
http\://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns/myns.xsd=extensiblexml/customtag/myns.xsd
http\://www.example.com/schema/core-commons-1.0.xsd=extensiblexml/example/core-commons-1.0.xsd
spring.handlers
http\://www.mycompany.com/schema/myns=extensiblexml.customtag.MyNamespaceHandler
http\://www.example.com/schema/core-commons-1.0=extensiblexml.example.CoreNamespaceHandler
小结:
要自定义Spring的配置标签,需要一下几个步骤:
使用XSD定义XML配置中标签元素的结构(myns.XSD)
提供该XSD命名空间的处理类,它可以处理多个标签定义(MyNamespaceHandler.java)
为每个标签元素的定义提供解析类。(SimpleDateFormatBeanDefinitionParser.java)
两个特殊文件通知Spring使用自定义标签元素(spring.handlers 和spring.schemas)































