在android中提供了常见的几种viewgroup的实现,包括linearlayout、relativeayout、framelayout等。这些viewgroup可以满足我们一般的开发需求,但是对于界面要求复杂的,这几个布局就显得捉襟见肘了。所以自定义的viewgroup在我们接触过的应用中比比皆是。
要想实现一个自定义的ViewGroup,第一步是学会自定义属性,这些自定义的属性将让我们配置布局文件的时候更加的灵活。自定义属性是在value目录下声明一个attrs.xml文件。
在这里我们声明了两个自定义属性集,CascadeViewGroup中的属性是针对我们自定义的CascadeViewGroup组件设置的,也就是可以在布局文件中
在编写代码前,我们还设置了一个默认的宽度和高度供CascadeLayout使用。这两个属性在dimens.xml定义。
10dp 10dp
下面开始编写自定义的组件CascadeLayout了。
package com.app.CustomViewMotion;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
* Created by charles on 2015/8/13.
*/
public class CascadeViewGroup extends ViewGroup {
//自定义布局中设置的宽度和高度
private int mHoriztonalSpacing;
private int mVerticalSpacing;
public CascadeViewGroup(Context context) {
this(context, null);
}
public CascadeViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);
}
public CascadeViewGroup(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup);
try {
//获取设置的宽度
mHoriztonalSpacing = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup_horizontalspacing,
this.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.default_horizontal_spacing));
//获取设置的高度
mVerticalSpacing = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup_verticalspacing,
this.getResources().getDimensionPixelSize(R.dimen.default_vertical_spacing));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
a.recycle();
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
final int count = this.getChildCount();
int width = this.getPaddingLeft();
int height = this.getPaddingTop();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View currentView = this.getChildAt(i);
this.measureChild(currentView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
CascadeViewGroup.LayoutParams lp = (CascadeViewGroup.LayoutParams) currentView.getLayoutParams();
if(lp.mSettingPaddingLeft != 0){
width +=lp.mSettingPaddingLeft;
}
if(lp.mSettingPaddingTop != 0){
height +=lp.mSettingPaddingTop;
}
lp.x = width;
lp.y = height;
width += mHoriztonalSpacing;
height += mVerticalSpacing;
}
width +=getChildAt(this.getChildCount() - 1).getMeasuredWidth() + this.getPaddingRight();
height += getChildAt(this.getChildCount() - 1).getMeasuredHeight() + this.getPaddingBottom();
this.setMeasuredDimension(resolveSize(width, widthMeasureSpec), resolveSize(height, heightMeasureSpec));
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean b, int l, int i1, int i2, int i3) {
final int count = this.getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View currentView = this.getChildAt(i);
CascadeViewGroup.LayoutParams lp = (CascadeViewGroup.LayoutParams) currentView.getLayoutParams();
currentView.layout(lp.x, lp.y, lp.x + currentView.getMeasuredWidth(),
lp.y + currentView.getMeasuredHeight());
}
}
public static class LayoutParams extends ViewGroup.LayoutParams {
int x;
int y;
int mSettingPaddingLeft;
int mSettingPaddingTop;
public LayoutParams(Context c, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(c, attrs);
TypedArray a = c.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup_LayoutParams);
mSettingPaddingLeft = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup_LayoutParams_layout_paddingleft, 0);
mSettingPaddingTop = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.CascadeViewGroup_LayoutParams_layout_paddinTop, 0);
a.recycle();
}
public LayoutParams(int width, int height) {
super(width, height);
}
public LayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams source) {
super(source);
}
}
@Override
protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() {
return new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT, LayoutParams.WRAP_CONTENT);
}
@Override
protected ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(ViewGroup.LayoutParams p) {
return new LayoutParams(p);
}
@Override
public ViewGroup.LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new LayoutParams(this.getContext(), attrs);
}
}代码稍微优点长,但是结构还是很清晰的。
1)构造方法中或者XML文件中配置属性的值。通过TypedArray中的方法获取我们在layout布局中设置的属性,并且将他们保存在成员变量中。
2)构造自定义的内部类LayoutParams。构造这个内部类,可以方便我们在测量我们的子View的时候保存他们的属性值,以便在Layout阶段布局。
3)generateLayoutParams()、generateDefaultParams()等方法。在这些方法中返回我们自定义的layoutParams。至于为什么要重写这些方法,可以查看ViewGroup类的addView()方法就很清楚了。

使用模板与程序分离的方式构建,依靠专门设计的数据库操作类实现数据库存取,具有专有错误处理模块,通过 Email 实时报告数据库错误,除具有满足购物需要的全部功能外,成新商城购物系统还对购物系统体系做了丰富的扩展,全新设计的搜索功能,自定义成新商城购物系统代码功能代码已经全面优化,杜绝SQL注入漏洞前台测试用户名:admin密码:admin888后台管理员名:admin密码:admin888
4)measure阶段。在measure阶段,我们会测量自己的大小,同时也要测量子View的大小,并且将子View的信息保存在LayoutParams中。
5)layout阶段。根据各个子View的信息,布局他们的位置。
最后加上布局文件。
实现的效果如下:
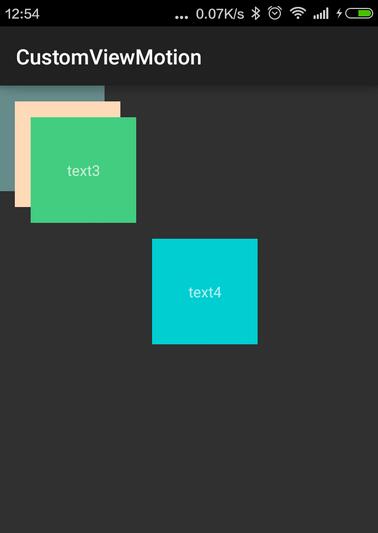
以上就是的全部内容,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持PHP中文网。
更多Android自定义ViewGroup的实现方法相关文章请关注PHP中文网!





























