一、XSS
跨站脚本攻击(cross site scripting),为不和层叠样式表(cascading style sheets, css)的缩写混淆,故将跨站脚本攻击缩写为xss。恶意攻击者往web页面里插入恶意script代码,当用户浏览该页之时,嵌入其中web里面的script代码会被执行,从而达到恶意攻击用户的目的。
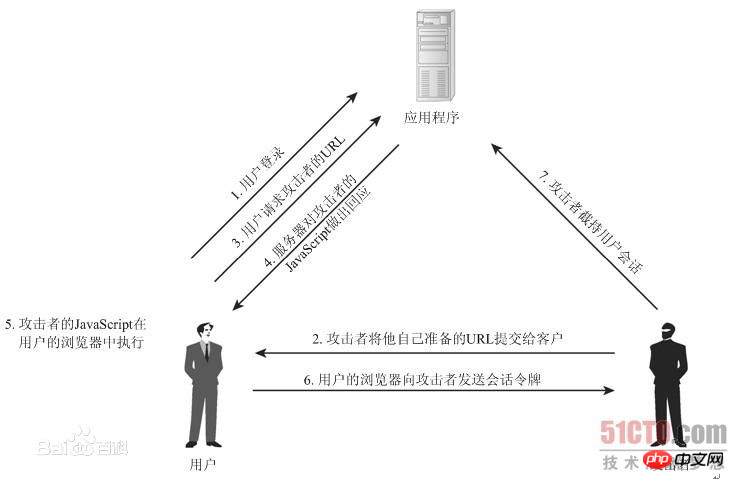
1. 工作流程
a. 恶意用户,在一些公共区域(例如,建议提交表单或消息公共板的输入表单)输入一些文本,这些文本被其它用户看到,但这些文本不仅仅是他们要输入的文本,同时还包括一些可以在客户端执行的脚本。如:
b. 恶意提交这个表单
c. 其他用户看到这个包括恶意脚本的页面并执行,获取用户的cookie等敏感信息。
2. 实例-未防范XSS攻击


1 pinglu = [] # 评论列表 2 3 #提交表单 4 def commit(request): 5 if request.method == 'GET': 6 return render(request, 'commit.html') 7 else: 8 com = request.POST.get('commit') 9 pinglu.append(com)10 return redirect('/index.html/')11 12 13 #查看评论页面14 def index(request):15 return render(request, 'index.html', {'commit': pinglu})

1 2 3 4 513 14Title 6 7 8评论
9


1 2 3 4 5Title 6 7 8评论
9 {% for item in commit %}10{{ item|safe }}11 {# item后加safe,默认数据安全,django不会做特殊处理#}12 {% endfor %}13 14
以上实例中,若在commit.html页面输入以下内容并提交:
则会在index页面执行此行代码,弹出警告框(若包含恶意代码,则会执行)

3. 防范XSS攻击
最直接的方法就是对于无法控制的输入在html页面内不要使用safe
{# {{ item|safe }}#}{{ item }}也可以在views里进行过滤,防止特殊字符提交到数据库或网页内
def commit(request):if request.method == 'GET':return render(request, 'commit.html')else:
com = request.POST.get('commit')if '16 30 